
You may have heard about digital assets and cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana, or Dogecoin, etc. Many people buy them as investments, hoping their value will go up, while others use them as a form of digital money.
They are becoming more popular every year, showing up in news headlines, social media, and even in conversations among friends, but what’s really behind the hype? Why are so many people talking about these digital coins, and what makes them different from regular money?
What is Crypto currency
Cryptocurrency has become one of the most talked-about topics in finance and technology. At its core, cryptocurrency represents a new form of digital money that operates independently of traditional banking systems. The most well-known cryptocurrencies include Bitcoin, which started it all, Ethereum with its smart contract capabilities, and Solana known for its fast transaction speeds.
Price volatility and investment concerns
The cryptocurrency market is known for its extreme volatility. One day you might see Bitcoin trading at $102,000, and the next week it could be at $98,000 or drop to $93,000. This unpredictability has created millionaires overnight while also causing significant losses for others who bought at the wrong time.
So, what exactly is cryptocurrency? How does it work? And what do terms like “blockchain” and “mining” mean? Let’s break down everything you need to know.
Definition and digital nature of Cryptocurrency

The word cryptocurrency comes from “crypto” (meaning hidden or secret, referring to cryptography) and “currency” (money). So, cryptocurrency is digital money that is secured by cryptography and exchanged through a computer network.
Because it’s digital, cryptocurrency has no physical form. Those golden Bitcoin coins you see in photos are just commemorative items or visual representations. The actual cryptocurrency exists only as data on computer networks, like the numbers in your bank account.
Traditional currencies like the U.S. Dollar and Euro are controlled by central banks. To send those currencies, you need a bank or payment service. But with cryptocurrency, you can send money directly to someone without needing a middleman like a bank.
Bitcoin's creation and philosophy

Cryptocurrency’s modern story began with Bitcoin, created in 2009 by an anonymous person known as Satoshi Nakamoto. Nobody knows who this person actually is, adding to Bitcoin’s legendary status.
Unlike traditional currencies controlled by governments, cryptocurrency was created to be free from central control. Some people didn’t like the idea of governments controlling money, so they made cryptocurrency as a way for people to exchange money directly with each other without needing any central authority.
Cryptocurrency was actually made to be used as money for buying, selling, sending, and receiving. However, most people don’t want to use cryptocurrency as currency due to its volatility. Imagine buying a coffee for 0.001 Bitcoin today, but tomorrow needing to pay 0.002 Bitcoin for the same coffee because of price changes. This made most people prefer traditional currency for spending and cryptocurrency for investment.
How Does Cryptocurrency Work?

Blockchain technology
Cryptocurrency works using a technology called blockchain. Imagine Donald has a notebook where every transaction is written down. Once written, it’s locked in and can’t be erased or changed. But not only does Donald have this notebook, everyone in this blockchain network has a copy, so no one can cheat. If Bob tries to change his notebook, it will be obvious because it’s different from everyone else’s.
Each page in the notebook is a “block” in the blockchain, and when one block is full, a new one is added to the chain. That’s why it’s called blockchain – a chain of blocks!
Transaction validation
When a new transaction is made, the transaction details are sent to a network of computers around the world. These computers check if the transaction is valid by solving complex puzzles. Once they solve the puzzle and confirm the transaction is correct, the information is added to blocks. These blocks are linked together, making the data permanent and unchangeable.
Mining and miners
People who solve these puzzles and validate transactions are called miners. When they solve the puzzles, the cryptocurrency system rewards them with new coins. This is called mining, based on a system called proof-of-work. That’s why you may have heard about Bitcoin miners using powerful computers – they want to solve as many puzzles as they can to earn more cryptocurrency.
Cryptocurrency as Investment
Investment potential and risks
Some people have made enormous profits by buying crypto when the price was low and selling when high. For example, if you bought Bitcoin in 2016 at around $500 per coin and sold it in 2024 at $60,000, you would have made a 13,000% return!
However, cryptocurrency is extremely volatile. If you bought Bitcoin at $45,000 in May 2022 and saw it drop to $16,000 by December 2022, you would have lost 65% of your money if you sold.
Why is crypto so volatile?
Crypto volatility comes from several factors: supply and demand, market sentiment, regulation changes, technological development, and market manipulation. The biggest drivers are speculation and media hype. Many investors buy cryptocurrencies hoping to make quick profits, often chasing trends without fully understanding the asset.
Key Cryptocurrency Terms
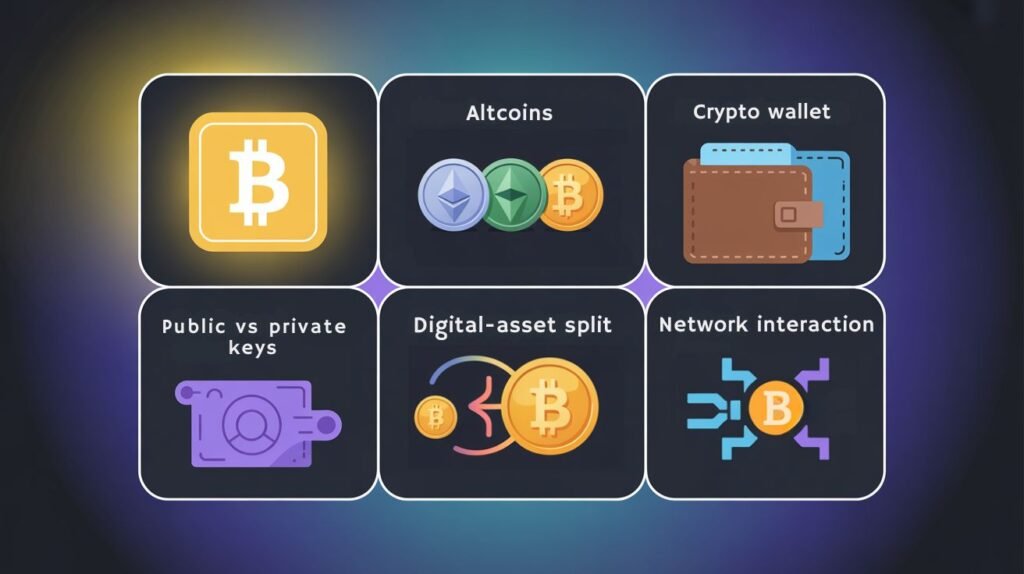
Bitcoin: The first and most well-known cryptocurrency, often called “digital gold” because it was the original and is still the most valuable.
Altcoins: Short for “alternative coins,” these are any cryptocurrencies that aren’t Bitcoin, including Ethereum, Solana, and meme coins like Dogecoin.
Cryptocurrency Wallet: Doesn’t actually store cryptocurrency (which stays on the blockchain) but stores your public and private keys. Hot wallets store keys online (convenient but vulnerable), while cold wallets store keys offline (safer but less convenient).
Public and Private Keys: The public key is like your wallet’s address that people use to send you cryptocurrency. The private key is like a password that proves you own the cryptocurrency. Share your public key freely, but keep your private key secret!
Fork: When a cryptocurrency splits into two versions because the community disagrees on improvements. For example, Bitcoin forked to create Bitcoin Cash.
Pros and Cons

Advantages
1) Decentralization: No single authority controls cryptocurrency, giving users more control over their money.
2) Accessibility: Anyone with internet access can participate without complicated bank applications, which is especially valuable for people without traditional banking access.
3) Flexibility: Send money anywhere, anytime, 24/7, without banks and with lower fees.
4) Privacy: More privacy than traditional banks, though transactions are still traceable if investigated.
5) High Return Potential: Many cryptocurrencies have increased in value by hundreds of percent, offering potential for significant profits.

Disadvantages
1) Extreme Volatility: Crypto prices can swing wildly, making you rich or poor in the same year.
2) Illegal Transactions: The privacy features make cryptocurrency attractive to criminals for money laundering and illegal activities.
3) Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments are still figuring out how to regulate cryptocurrency, creating uncertainty about future use.
4) Scams: Many fake cryptocurrency websites and schemes lure people with false promises, and once you transfer crypto to scammers, it can’t be reversed.
5) Lack of Consumer Protection: No one controls cryptocurrency, so when something goes wrong, there’s no one to help. Transactions are irreversible, unlike traditional banking where you can dispute charges.

Conclusion
Cryptocurrency offers exciting opportunities for those willing to learn about its potential. Whether you should use cryptocurrency depends on your risk tolerance and financial goals. If you’re interested, it’s crucial to do your research first and avoid falling into FOMO by jumping in without knowledge.
Don’t rely solely on any single guide to make decisions. Start small, learn continuously, and never invest more than you can afford to lose. The cryptocurrency space is full of opportunities but equally full of risks. Education is your best protection against making costly mistakes.
Whether you choose to invest in cryptocurrency or simply want to understand this revolutionary technology, the key is to stay informed and make decisions based on knowledge rather than hype. The future of money is evolving, and cryptocurrency is playing a major role in that evolution.


